ERREUR 4: Croire qu’il faut respirer plus pour s’oxygéner plus
Avertissement: Consultez obligatoirement votre médecin pour votre santé.
Références:
Beall 2007. Two routes to functional adaptation: Tibetan and Andean high-altitude natives
Iscoe et.al. 2011. Supplementary oxygen for nonhypoxemic patients: O2 much of a good thing?
Massabuau 2003. Primitive, and protective, our cellular oxygenation status?
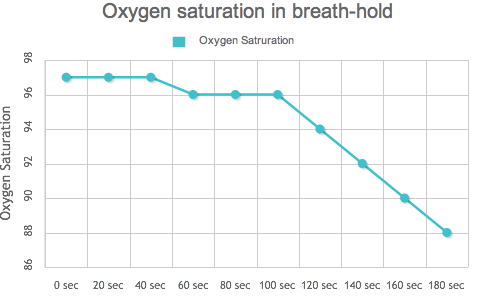
Votre saturation d'O² chute seulement après 100 secondes d'apnée (étude scientifique ci-dessus : Laurino et.al. 2012).
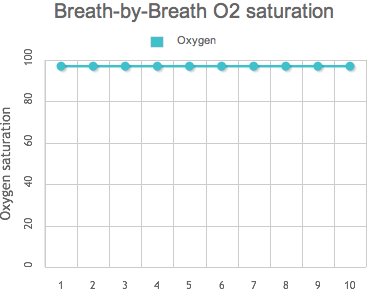
A chaque inspir/expir, votre saturation en oxygène reste maximale.
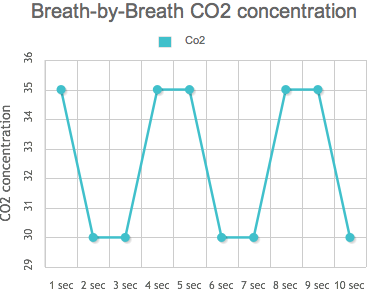
Votre respiration régule principalement votre concentration en CO2.